New catalyst for inducing same oxidation reaction under illumination even in the dark
Can oxidize formic acid in the dark
Overview
Photocatalysts are materials that induce redox reactions under illumination. In particular, it is effective for downhill reactions (oxidative degradation of hazardous and pollutants) and titanium oxide (TiO2) which is UV light responsive, is already in practical use. However, TiO2 photocatalytic technology is limited to small amounts and low concentrations of substances based on the solar light spectrum, and there is a problem that oxidation degradation treatment similar to that under illumination is never induced in the dark conditions.
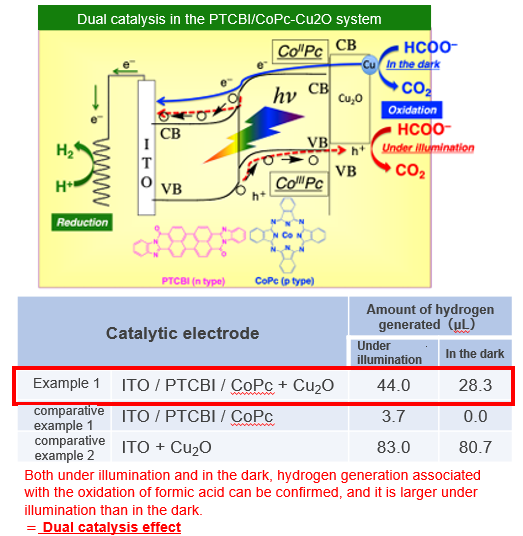
In his research for application as a photoelectrode and photocatalyst for organic p-n junctions, the inventor found that organic p-n junctions can catalyze (= dual catalysis) the oxidation of thiols even in the dark conditions [1]. In addition, as a result of his intensive research, he succeeded in expanding the target of dual catalysis to formic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and hydrazine by supporting a cocatalyst on organic p-n junctions.
Dual catalysis is a new type of catalysis that TiO2 does not have. The selection of organic p-n junctions and co-catalysts is expected to expand the application range and market size of catalysts for environmental purification applications.
Cu acts as a cocatalyst and oxidizes formic acid even in the dark
Product Application
・Catalysts for environmental purification
・Complementation of titanium oxide
Related Works
[1] J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 7445
IP Data
IP No. : JP7399423
Inventor : ABE Toshiyuki, WATANABE Ryuhei
keyword : photocatalyst, downhill reaction, titanium dioxide, formic acid, dual catalysis
