Methods to promote EPS production by bifidobacteria
Bifidobacterium strains that produce high levels of extracellular polysaccharides by fucose
Overview
Extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) produced by some of the dominant bifidobacteria in the infant intestine are expected to improve intestinal immune resistance and protect against infection. However, mass cultivation of bifidobacteria, which are obligate anaerobes, is expensive, and it is difficult to extract only the useful EPS in large quantities.
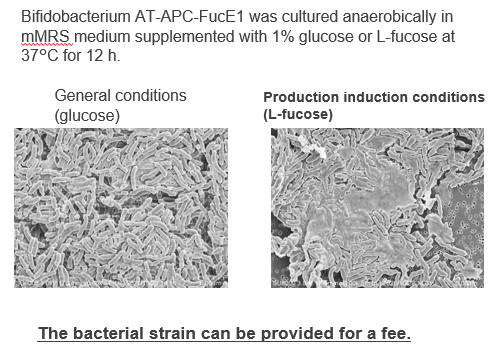
The present invention relates to a method for promoting the EPS production of a specific bifidobacterium by the addition of L-fucose, which is abundant in marine algae and the like. Bifidobacterium breve strain AT-APC-FucE1, which was selected and isolated from infant feces on the basis of L-fucose utilization, exhibits a characteristic that the EPS production is stimulated inducibly when L-fucose is added compared with normal culture conditions (right panel).
Examples of applications of the present invention include the use as a research tool for the analysis of the EPS production mechanism of bifidobacteria in addition to the development of functional fermented foods, intestinal control agents, and supplements that promote the intestinal EPS production.

Induction of Bifidobacterium EPS Production by Fucose Addition
Product Application
・Fermented food
・Probiotics
・Supplements
IP Data
IP No. : WO2023/048126
Inventor : Wakako Otsubo et al.
keyword : Bifidobacterium, EPS, exopolysaccharide, fucose, Probiotics
