Rhizobia that reduce soil N2O
Possible to reduce greenhouse gas in agricultural land!
NEDO Moon shot R&D project
Overview
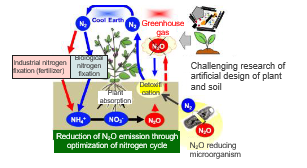
Dinitrogen monoxide (N2O) is an intense greenhouse gas having about 300 times greater effect than carbon dioxide (CO2). It is said that 59% of anthropogenic emission comes from agriculture.
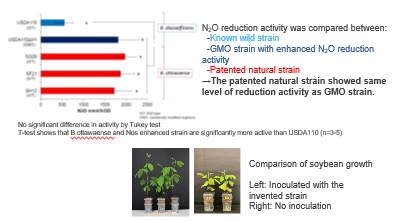
In particular, chemical fertilizer overuse in large scale agriculture is a cause of N2O emission from the soil since more chemical fertilizers are applied than the absorption by plant. A certain rhizobia (Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110) is known to reduce N2O to harmless nitrogen (N2), but the bacteria are not effective enough to solve the problem. In the context that non GMO rhizobia usage with high N2O reductase activity is expected from the viewpoint of global warming control and soil ecosystem, this invention proposes a natural rhizobia (Bradyrhizobium ottawaense SG09, etc.) with stronger N2O reductase activity than the conventional rhizobia, and its application.
Features・Outstandings
Product Application
・Microbial material
・Fertilizer
・Growing soil
Related Works
[1] Itakura et al. 2013. Nature Climate Change 3: 208-212. DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1734
[2] Sánchez et al. 2017. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2017 9: 389-396. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12543.
[3] Wasai-Hara et al. 2020. Microbes Environ. 35: ME19102. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME19102.
IP Data
IP No. : WO2022/149590
Inventor : MINAMISAWA Kiwamu, HARA Sawa, ITAKURA Manabu, ARTHUR FERNANDES SIQUEIRA
keyword : Agriculture, Food item
