Mg2Si thermoelectric conversion film with reduced thermal conductivity while keeping electrical conductivity
Mg2Si film with high porosity and uniform vacancies
Overview
The development of thermoelectric conversion technology to extract
electricity from waste heat is being actively pursued. Mg2Si is a
thermoelectric conversion material suitable for the use of industrial waste
heat since the thermoelectric conversion efficiency achieves its
maximum value at around 300ºC environment.
However, the heat is often leaked due to its high thermal conductivity
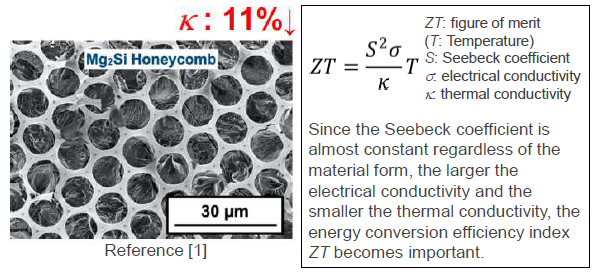
so the conversion efficiency is not as high as expected (cf. right formula).
There is a report that the thermal conductivity was decreased by
compacting Mg2Si powder into pellet and making it porous, but since the
electrical conductivity was also reduced due the grain boundary, the
conversion efficiency was not increased.
This invention is about a Mg2Si porous film that solves the above issue.
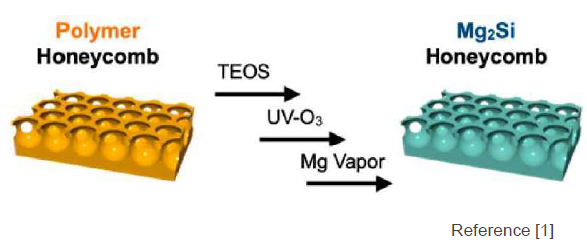
Low thermal conductivity by honeycomb-like highly porous film
Product Application
The present porous Mg2Si film shows the same electrical conductivity (~2 S/cm) as an ordinary Mg2Si thin film such as sputtered film, but the thermal conductivity is reduced by 11% even with a single porous structure layer. Therefore, it is possible to realize a thermoelectric conversion device by increasing film layers with less thermal leakage in the waste heat range around 300ºC.
Related Works
[1] Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 10176.
IP Data
IP No. : JP2020-145374
Inventor : YAMADA Takahiro, YABU Hiroshi, MATSUI Jun
keyword : Environment, Energy
