PPARα agonists that improve cognitive function
New drug discovery seeds for psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia
Overview
Recent large-scale genomic and postmortem brain analyses have indicated that synaptic dysgenesis may be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia, but the detailed mechanisms remain unclear. Drugs mainly blocking dopamine D2 receptors have been used for the treatment of schizophrenia, but they are mainly used for symptomatic treatment and have insufficient effects on negative symptoms and cognitive dysfunction. Therefore, it is desirable to develop new drugs based on new molecular mechanisms.
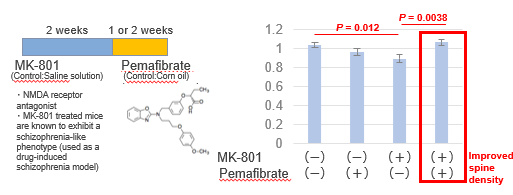
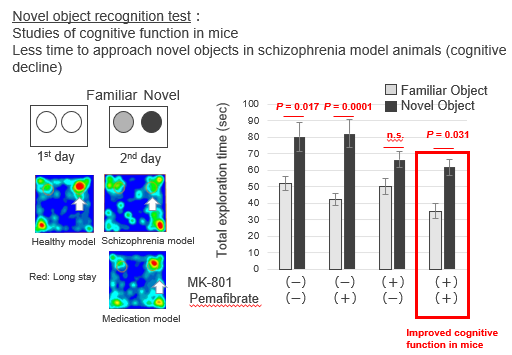
The inventors have discovered that the decreased function of the PPARA gene, which encodes the nuclear receptor PPARα, is involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia [1]. Since PPARα is a transcription factor that can be activated by its ligand, they considered the possibility that activation of PPARA might lead to the improvement of schizophrenia, and found that fenofibrate, a PPARa agonist, is actually effective in improving synaptic function [2]. In this study, they found that pemafibrate, a PPARa agonist, helps to improve cognitive function at the same time as restoring spine density in mice. The invention could lead to the discovery of novel mechanisms for schizophrenia. Furthermore, since decreased spine density and cognitive decline are similar symptoms in other psychiatric disorders such as Alzheimer's, it could also be a therapeutic agent for these disorders.
Spine density evaluation test in mice
Assessment of cognitive function in mice
Product Application
・Drugs for schizophrenia
・Other therapeutic agents for psychiatric disorders
・Drugs for Alzheimer's dementia
Related Works
[1] Maekawa M, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2017; 7:e1229.
[2] Wada Y, et al. EBioMedicine, 2020; 62:103130.
IP Data
IP No. : PCT/JP2023/023819
Inventor : MAEKAWA Motoko, OWADA Yuji
keyword : PPAR, Psychiatricdisorders, Schizophrenia, Alzheimer'sdementia, Drugdiscovery abroad
