Open type Nanoporous body, surface treatment, composite
There are many examples such as stainless steel (austenitic and ferritic), nitinol, Si, C, Fe, W, Ti, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ta, Fe-Cr-Co-Ni-V high entropy alloy, Ni-Mo alloy, Fe-Al alloy, etc.! Depending on the application, magnesium and iron composites can also be made!
Overview
Conventionally, for porous metals (Nano-microporous metals) having micropores of nano or micrometer size, a dealloying (deconditioning) method has been used to obtain porous bodies by corrosion-removing only noble metals from alloys of noble and noble metals in aqueous solution. However, there is a problem that the target metals are limited in that it is possible to fabricate nano-microporous metals only in noble metals and their alloys with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode potential.
The present invention can easily fabricate nano-microporous bodies in vulgar metals and their alloys that could not be fabricated in principle by conventional methods. As one specific example, the nano-porous bodies were successfully fabricated in pure metals such as titanium, niobium, and molybdenum, alloys such as beta titanium and stainless steel (austenitic and ferritic), and carbon.
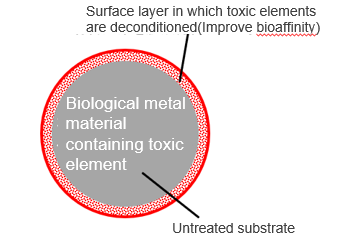
Features・Outstandings

Product Application
・Catalyst
・Electrode
・Filter
・Medical material
・Sensing material
・Composite material
Related Works
[1] Materials Letters Volume 65, Issue 7, 15 April 2011, Pages 1076-1078
[2] Materia Japan Vol. 52 No. 8 (2013) "Development of Open-Cell Porous Materials with Base and Semimetals and Their Alloys"
IP Data
IP No. : US 9,279,186, JP5678353, DE112010005201.84, JP2022-140750
Inventor : KATO Hidemi, WADA Takeshi, other.
keyword : Material, Environment, Energy
