An inhibitor of Influenza A virus: tFIT-DPQ probe
Over 1000 times affinity to bind with RNA virus (vs. DPQ)! Promising diagnostic and inhibitory drug!
Introduction
Influenza prevails broadly every season. Current diagnostic drugs can not be performed until the virus increases quite a lot (ca. 12~24h after infection, symptoms may appear), and if not so, both sensitivity and accuracy of the test will be doubtful. To prevent on-going severe symptoms, new diagnostic tech for influenza at earlier stage becomes so demanded. This invention provides a conjugate of peptide nucleic acid sequence (PNA) and a small molecule, targeting the commonly identical RNA hairpin promoter region of eight kinds of influenza A virus.
Effect & Application
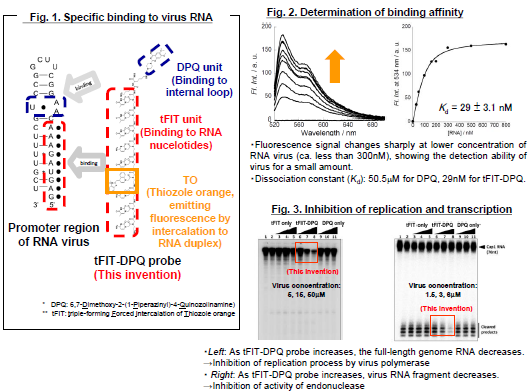
The conjugate (tFIT-DPQ probe) is composed of two parts:
tFIT unit for recognition of virus RNA’s nucleotides and DPQ*
unit for UAA internal loop binding. In tFIT unit, a fluorescent
ligand is inserted so as to be capable to emit signals when
intercalating to RNA duplex (Fig. 1). The conjugate shows an
over 1000 times greater binding affinity than DPQ molecule
only (Fig. 2). By simply mixing the virus RNA contained
sample and the conjugate together, test result will be obtained
within a short time (ca. 2~3 min) and 1nM virus RNA (ca. 1010
copies) can be detected. Moreover, the virus inhibition effect
by the conjugate in micromolar range was confirmed (Fig. 3).
tFIT-DPQ probe is expected to be applied as diagnostic and
inhibitory drugs, as well as a screening tool for influenza drug
candidates.
* Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 368.
Structure of tFIT-DPQ probe and its virus inhibition effect
IP Data
IP No. : JP2019-141527
Inventor : SATO Yusuke, NISHIZAWA Seiichi, TANABE Takaaki, KAWAGUCHI Atsushi
keyword : influenza, diagnostic drug
