Titanium alloy for biomedical application
High antibacterial property, biocompatibility and a low Young's modulus close to the cortical bone
Overview
A requirement for biocompatible Ti alloy for orthopedic implants is
to suppress stress shielding, which occurs because of the large
difference between Young’s moduli of the prosthetic stem and the
cortical bone (10–30 GPa). Meanwhile, conventional autoclave
sterilization before implant exhibits the discoloration and heaviest
particulate contamination, and some multiple sterilization regimens
for metallic materials may pose serious biological concerns.
The present invention can provide the necessary functions to a Ti
implant material without impairing the low Young's modulus of Ti
alloy. It possesses high antibacterial properties with a high
antibacterial activity value above 2.0 from the antibacterial test (JIS
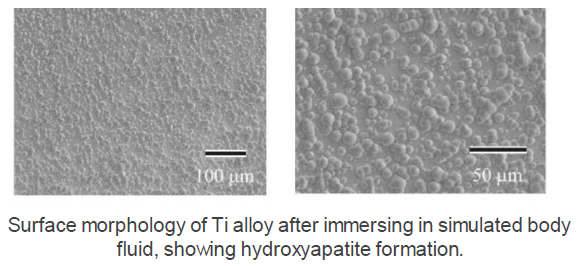
R 1702) and osseointegration fromhydroxyapatite formation on the
surface of Ti alloy in simulated body fluid.
Features・Outstandings

Product Application
・Titanium alloy for biomedical use, especially for artificial prosthetic stem.
Related Works
[1] S. Hanada, N. Masahashi, T.K. Jung, S. Semboshi, Mater. Sci.
Eng. A 802 (2021) 140645.
[2] MASAHASHI Naoya, MORI Yu, TANAKA Hidekazu, KOGURE
Atsushi, NORO Atsushi, KAMIMURA Masayuki, YAMADA
Norikazu, ITOI Eiji, HANADA Shuji, Titanium, 34 (2016) 216-221
IP Data
IP No. : JP2021-074013
Inventor : MASAHASHI Naoya, HANADA Shuji, MOKUDAI Takayuki, ITOI Eiji, MORI Yu, INOUE Hiroyuki
keyword : Material, Medical/Welfare device
